Default checks
Each new application receives default checks such as DNS, SSL, WAF, Header, and Uptime.
Check types
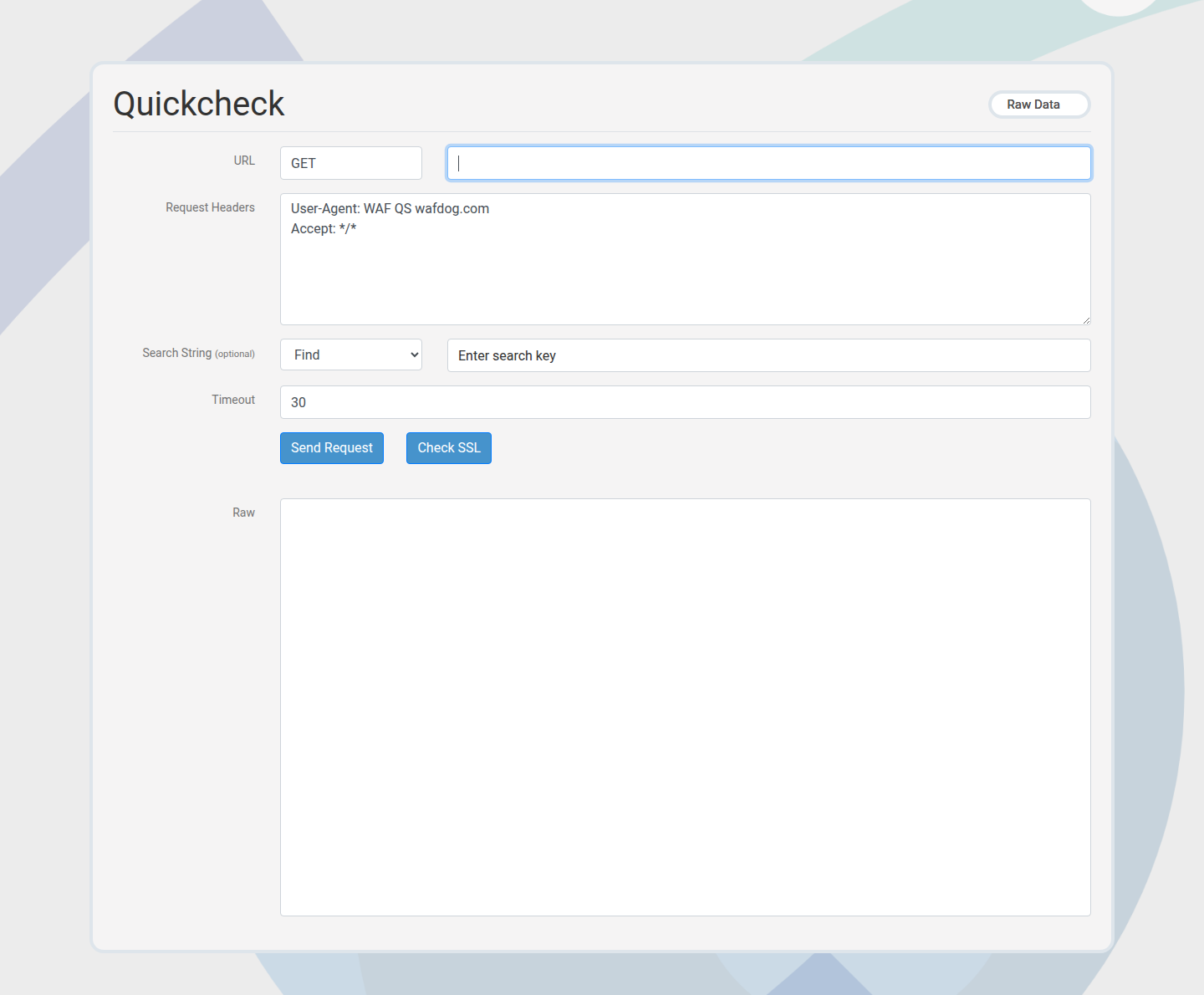
Simple HTTP
Custom checks for critical endpoints, APIs, or login pages. Use them for precise expectations that default checks do not cover.
- Configure method, path, headers, optional body, and search string rules.
- Pass/fail is based on the configured expectations and response content.
DNS
Validates that hostnames resolve and reports record details.
- Surfaces A/AAAA/other records, TTL, and provider hints.
- Fails when no usable records are returned.
SSL
Inspects the certificate chain and expiry to ensure TLS hygiene.
- Highlights expiry windows, chain completeness, and hostname matches.
- Use this to catch expiring or misconfigured certificates early.
WAF
Tracks whether your WAF blocks expected payloads and whether behavior changes over time.
- Uses a baseline request plus probes to detect blocking changes.
- Pair with WAF profiling for deeper payload coverage.
Header
Scores the presence and quality of security headers.
- Highlights missing or weak headers that reduce browser protections.
- Some headers are legacy (for example Expect-CT) and may be informational only.
Uptime
Monitors availability and reports uptime trends over time.
- Use shorter intervals for critical paths when faster detection is required.
Checks overview
Use the checks list to review all checks in the active project, including status, type, and last run time.
Check detail
Each check has a detail view with the latest result, check state, and history buckets.
Create a custom check
Use custom Simple HTTP checks to cover critical endpoints and custom rules.
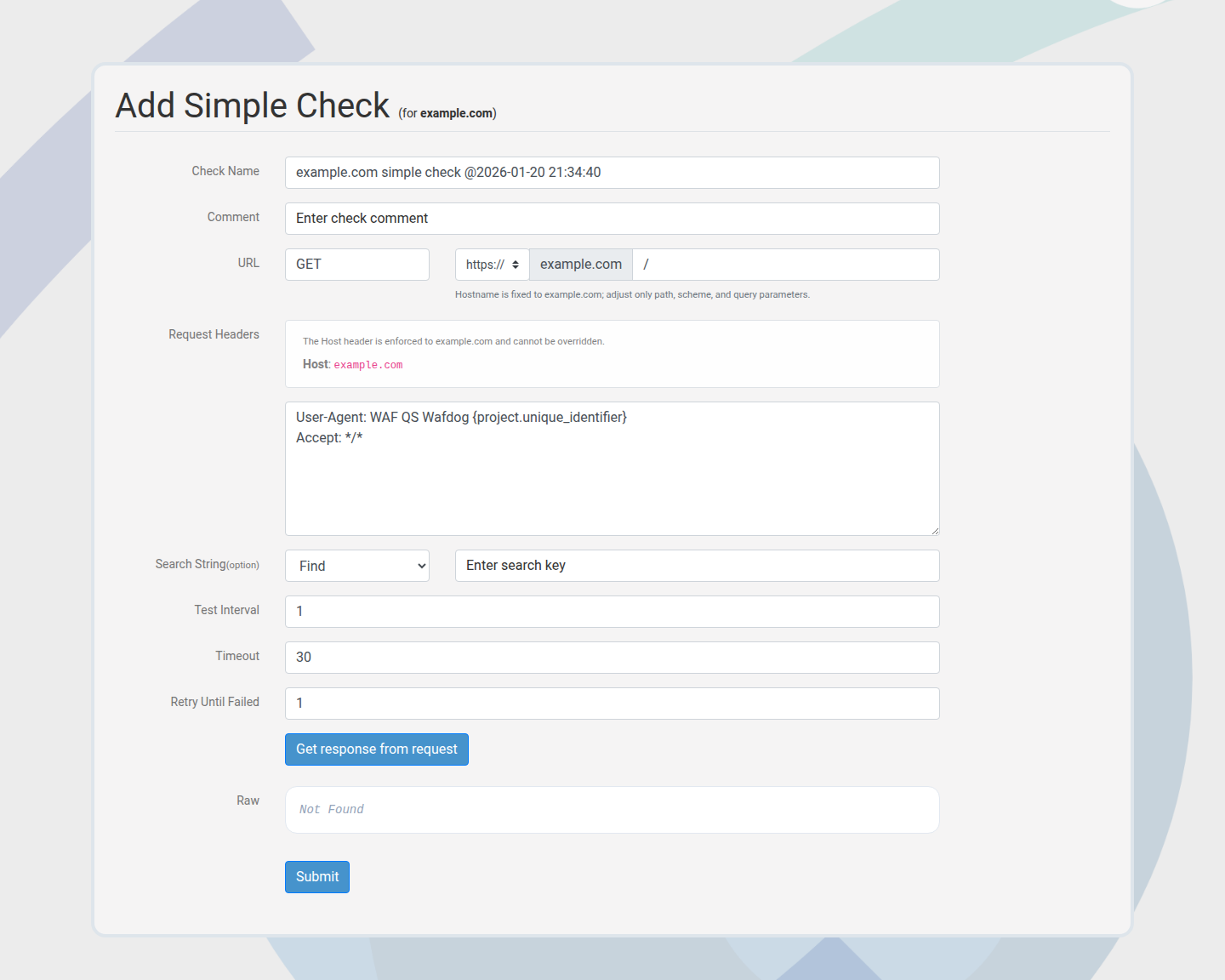
Scheduling and intervals
Checks run on configured intervals. Shorter intervals increase detection speed and credit usage.
Tuning and false positives
- Use Simple HTTP search strings to verify the exact content you expect.
- If a WAF baseline changes after a release, recheck or profile again to confirm the new behavior.
- Header checks may include legacy headers; treat those as informational where appropriate.
Run checks now
Manual rechecks are useful after deploying changes or resolving incidents.
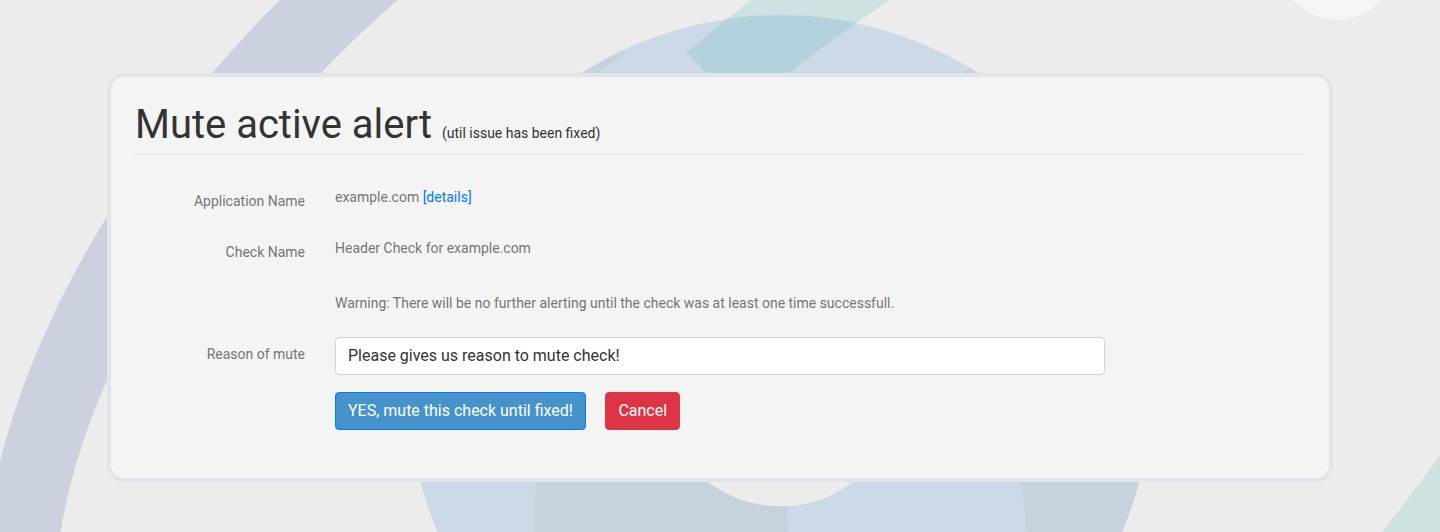
Mute alerts
Mute suppresses alerts while keeping checks active. Provide a reason and duration.
History and buckets
Historical views help identify flapping, regressions, and stability trends.
Member Quickcheck
Member Quickcheck runs an ad-hoc check without persisting it as a permanent check.